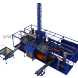
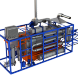
Pyrolysis is defined as a thermal conversion process of organic waste in the oxygen-free environment. The main products resulting from the processing of hydrocarbons are synthetic gas, a liquid oil and solid residues (biochar, carbon black, metal).
Pyrolytic process, also known as cracking, reads as follows:
- The source material is continuously fed into pyrolysis chamber from the hopper/by the pump.
- The pyrolysis chamber is heated by the mixed fuel burner installed in furnace.
- Liquid fuel is used for the plant startup. It is self-fed from fuel tank to the burner.
- After the startup the burner capacity is lowered and heating is carried out on pyrolysis gas.
- Vapor and gas mix is cooled in the condensation system, then in heat exchanger by recirculation.
- Vapor and gas mix product is fed from the heat exchanger to the gas-liquid separator where flows are separated.
- Liquid fuel is drained to receiver tank, then enters the fuel tank or to the storage.
- Gas is fed to the burners.
- Dry residue is discharged by screw conveyor to the air tight hopper, where it cools and further to the storage bin.
Get to know more about TDP-2-800 plant process description.
Advanced features presented by pyrolysis technologies implemented in TDP-2-800:
- Nonconventional power sources recovery
- Automatic control system
- High-powered efficiency
- Nominal emissions
- Small system size
- Low energy consumption
- Economically viable process
When using the material or any part of it the link to the website (www.i-pec.ee) is required